Quality assurance interview questions in the pharma industry:
Before knowing the interview questions for QA job, you have to know the situation in interview pattern. Here we have provided the question and answers according to Quality assurance department point of view. But in actual times there is no rule to ask these type of questions only. Because you are a fresher and you have all the subjects in your B pharmacy like pharmaceutical analysis, pharmaceutics and medicinal chemistry etc.
They may expect answers form you for other HPLC, UV etc principles methodology also. For your understanding about QA job and knowledge required for this job, we have provided QA job oriented knowledge related questions here.
You have to know the Quality control interview questions also before attending an interview for getting success.
Quality assurance interview questions in pharma industry are as follows
1. Define quality assurance
Ans) QA is a broad range of concept contains all the matters that individually or collectively effect the quality of a product. QA mainly concentrated on planning and documenting the procedures to assure the quality of the product.
2. Explain the difference between QC and QA?
Ans) QA provides the confidence that a product will full fill the quality requirements. QC determines and measures the product quality level.
3. Expand cGMP and what is the difference between GMP and cGMP?
Ans) cGMP known as Current Good Manufacturing Practices. It is a USFDA regulations to assure proper design , manufacturing and control of manufacturing processes and services.
GMP-Good Manufacturing Practices. These are the standard guidelines given by Food and Drug administration to make sure that a product is manufactured with safety and quality. c in cGMP means current. It refers to recent and advance updates to these standard guidelines. cGMP is up to date standard reference guidelines.
4) Tell me any five countries with their regulatory authorities?
Ans) India – Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO)
USA – United States Food and Drug Administation (USFDA)
UK – Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA)
Japan- Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare (MHLW)
Australia- Therapeutics Goods Administration (TGA)
Brazil- ANVISA
5) Expand ICH? Tell me about ICH Guidelines?
ICH known as The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. It brings the regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical companies together to discuss the drug registration technical aspects.
The aim of the ICH is to enhance the harmonisation world wide to make sure that safe, high quality and effective drugs are developed and registered in the most efficient manner.
ICH provides guidelines on 4 aspects that is quality , safety , Efficacy and Multidisciplinary guidelines.
6) What is SOP?
SOP known as Standard Operating Procedure.
7)Expand IQ OQ PQ DQ
IQ- Installation Qualification
OQ-Operational Qualification
PQ-Performance Qualification
DQ-Design Qualification
8) Difference between validation and calibration
Validation produces the documented evidence assuring a specific procedure/procedure or activity consistently develops a product with predetermined specifications and quality credits. It is performed according to validation protocol.
Calibration denotes that an equipment produces the values in specified limits by comparing the values produced by a standard. It is done according the calibration standard operating procedure.
9) Expand BMR and BPR?
Ans) BMR – Batch Manufacturing Record , is prepared as a written file during the manufacturing a product by writing. Step by step manufacturing process and details about batch recorded here.
BPR Batch Packaging Record, is kept for every BMR. BPR is depends on packaging operation.
10) What do you know about stability studies?
Ans) These are necessary for developing the pharmaceutical products. It helps to evaluate the effect of environmental factors (e.g Light, Humidity, Temperature etc) on Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient(API) or Pharmaceutical formulation.
11) What is the time period required for long term and accelerated stability studies?
Ans) Long term 12 months, Accelerated studies- 6 months
12) What are types of climatic zones? India belongs to which climatic zone?
Ans) India belongs to Zone III(Hot dry zone) and Zone IVb(Hot/Higher humidity)
FYI
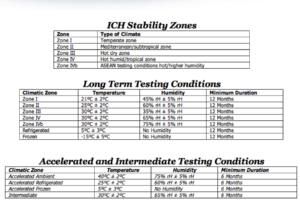
I have also prepared some more important questions for you from QA of point view. You can view QA interview questions in pharmaceutical industry here.
Please share your opinion below
